2000V Higher voltage megapage
News | 2025-10-15
Follow Us
2000V Higher voltage megapage
1. Introduction to High-Voltage Rectifiers
1.1. What is a 2000V Rectifier?
A 2000V rectifier is a specialized diode for converting AC to DC within electrical systems operating at very high voltages.
These work by allowing current to flow freely in one direction while blocking it almost completely in the reverse, with the listed voltage designating the maximum reverse voltage (VRRM) the diode can repeatedly withstand.

Image: WeEn Semiconductors’ series of 2000V rectifiers achieve a 5% reduction in forward voltage drop (VF) and a 20% improvement in thermal resistance.
A 2000V rectifier is built for robust, high-stress environments and has been created to undergo very significant reverse voltage potentials, making it an essential building block for in EV charging and renewable energy generation, as well as for industrial machinery, medical equipment, and advanced consumer electronics.

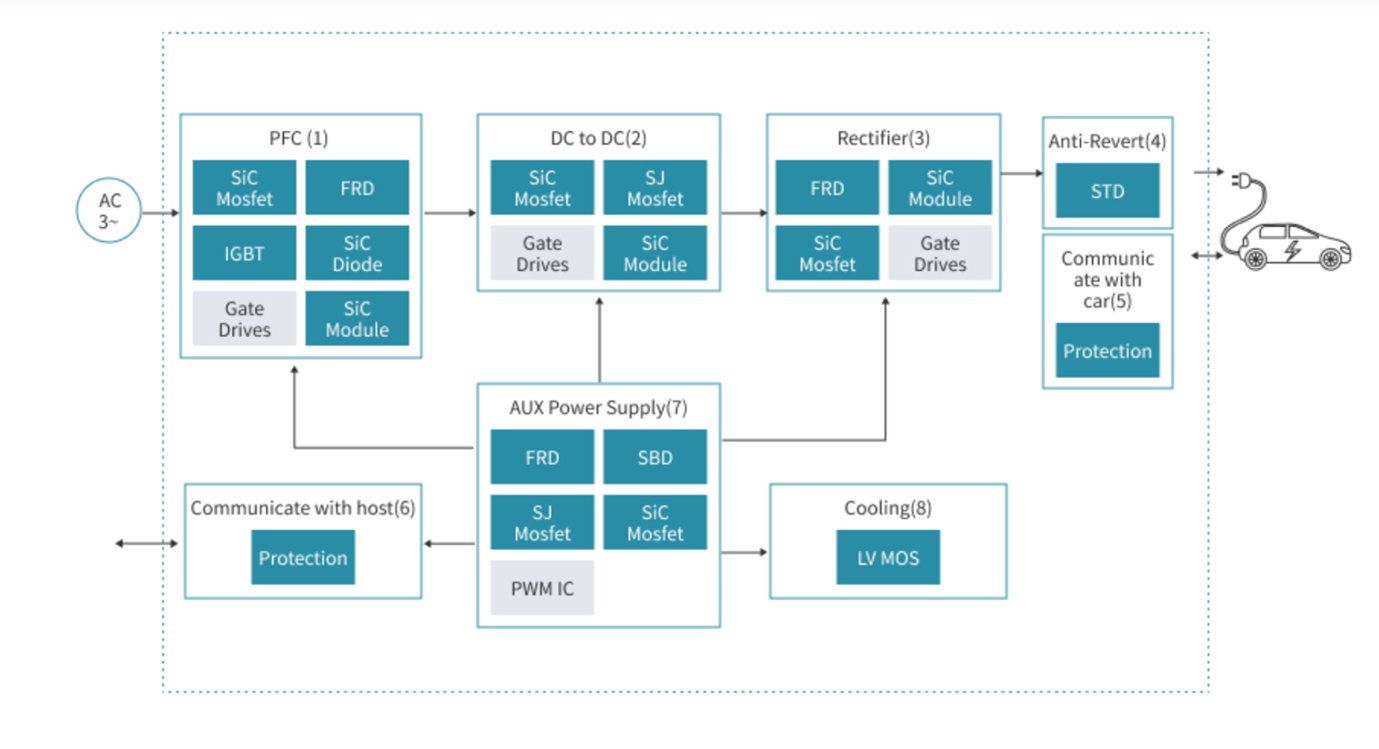
Image: Power semiconductors manage the flow of electricity between the grid and the vehicle, helping to minimize energy loss, improve charging efficiency, and ensure reliable system performance. They also safeguard the battery against voltage spikes and overheating, supporting longer battery lifespan and safer charging overall."
1.2. Why are 2000V Rectifiers Critical in Modern Electronics?
The growth of the 2000V rectifier market is driven by the global demand for higher efficiency and greater power density, especially in the renewable energy and electric vehicle (EV) sectors. As system voltages increase to improve performance, components with a higher voltage rating become essential for ensuring safety and reliability.
In applications like 800V EV on-board chargers or 1500V solar inverters, operating at higher voltages reduces the amount of current needed for the same power output. This drastically cuts down on energy lost as heat (P=VF*IF).
Using a higher voltage rectifier also allows for the use of thinner, lighter cables and results in smaller, more efficient, and more cost-effective systems. The safety margin offered by these components also mitigates the risk of potential voltage spikes, which is especially essential in renewable energy generation.
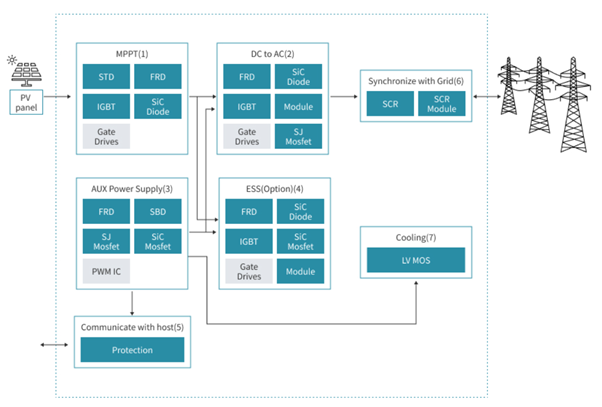
Image: The graph illustrates how power semiconductors contribute to the operation and efficiency of PV inverter
At centralized EV charging stations, the charger located farthest from the power source can have cable lengths of 20–30 meters. Rapid load changes in such long lines can result in significant stray inductance, which may cause (>1700V) high voltage spikes that can damage the ORing diodes and requires mitigation techniques, with 2000V Oring diodes being an effective method.
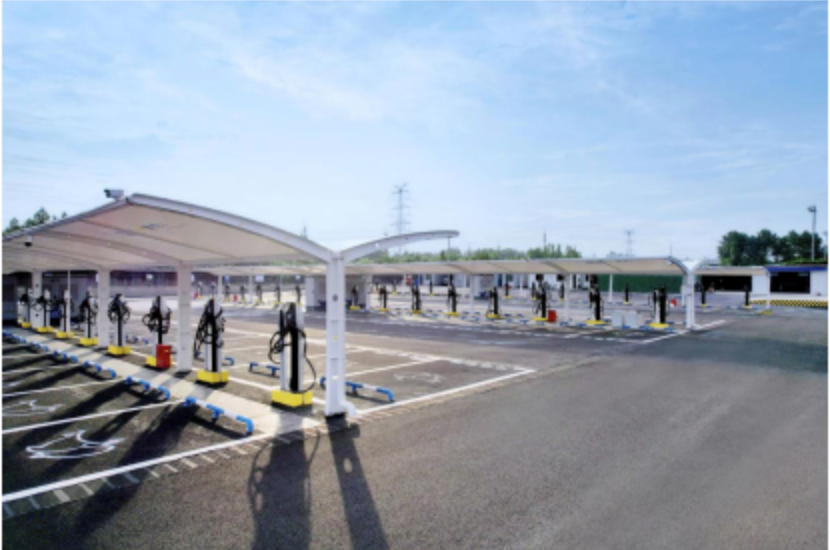


Figure: a 1700V voltage pulse measured at an EV charging station
2. Key Performance Metrics for 2000V Rectifiers
2.1. Electrical Efficiency and Switching Performance
An applications' efficiency and reliability are directly affected by performance metrics of the rectifier. For designers of EV chargers or solar inverters, understanding these parameters is key to meeting strict performance targets. The most important metrics are forward voltage (Vf), and leakage current (Ir).
2.1.1. Forward Voltage
This is the small voltage drop seen when the rectifier is on and conducting current. This voltage drop results in a conduction loss and a lower Vf value is always better.
2.1.2. Leakage Current
This is the small current that flows backward through the rectifier when the off/blocking state. This contributes significantly to standby power consumption and adds to the system's heat load, especially at high operating temperatures. In high-voltage systems, a low leakage current is crucially important in maximizing efficiency.
2.2. Thermal Performance and Reliability
A rectifier's ability to manage heat is as important as its electrical efficiency. Poor thermal performance will reduce the reliability and lifespan of the entire power system. Key metrics for thermal performance and robustness include operating junction temperature (Tj, max), thermal resistance (Rth), and avalanche capability.
2.2.1. Operating Junction Temperature
This is the maximum internal temperature that the rectifier's semiconductor can safely handle during operation. A higher Tj, max rating provides a greater safety margin and improves device lifetime and rectifiers with this will be more robust and reliable in high-temperature environments, such as inside a sealed EV charger.
2.2.2. Thermal Resistance
This metric shows how well heat can be transferred away from the internal semiconductor junction. A low thermal resistance enables a cooler device and therefore enables smaller, and lower cost heatsinks to be used.
2.2.3. Avalanche Capability
This measures the rectifier's ability to survive brief over-voltage events. A high avalanche capability is particularly important in applications like renewable energy generation (solar, wind etc) where voltage spikes can commonly occur as it protects the device from catastrophic failure.
3. Common Applications of 2000V Rectifiers
3.1. DC Fast Charging Systems
These high-power stations have been created to deliver DC directly to the vehicle's battery for faster charging – with modules of high-power 2000V rectifiers converting the AC grid power into a high-voltage DC output. Thermal performance and efficiency are essential, with low-loss rectifiers enabling faster power delivery and reliability.
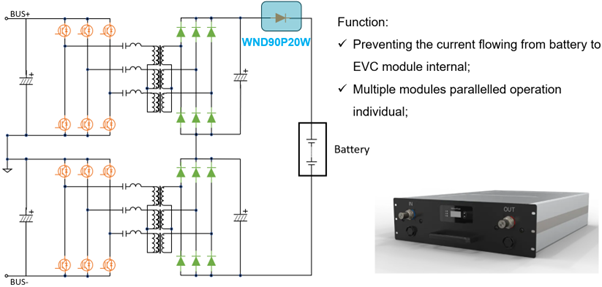
Image: a typical DC-DC stage of an EVC module
3.2. On-Board Chargers (OBCs) in Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The automotive industry is shifting towards 800V and higher voltage architectures, and this is creating a significant market driver for 2000V and higher voltage rectifiers.
Operating at higher voltages not only reduces vehicle weight (as above, through the use of smaller cables) but also allows for significantly faster charging times. This improved charging time is vital in reducing charging anxiety and helping adoption. These rectifiers are a critical component in both on-board and off-board charging systems.
The OBC converts the AC from a standard charging point to the DC required for charging the main battery.
As above, the 2000V rectifier's higher voltage rating gives a crucial safety margin against power grid fluctuations and their high efficiency minimises energy loss and heat buildup within the charger's sealed enclosure, improving overall reliability.
3.3. Renewable Energy Generation
For renewable generation, system voltages have increased to 1500V and even higher to maximize efficiency. As raising the voltage allows the current to be lowered, higher voltage rectifiers reduce the power lost in the long cables from the solar panels or wind turbines.
3.3.1. Solar Power Inverters
For PV generation, solar inverters are needed to convert the DC electricity coming off PV arrays into AC for the grid. Rectifiers are used within the inverter to safely manage the high (1500 VDC) input voltages that are used by utility-scale solar farms. Using 2000V rectifiers ensures lower energy losses and higher efficiencies with more power sent to the grid.
3.3.2. Wind Turbine Converters
Unlike solar panels, wind turbines generate AC, however this power is variable and needs to be converted to grid-compliant frequencies – either 50 or 60 Hz, depending on the country. Power converters inside wind turbines are responsible for this process, which starts by rectifying the generator's output to high-voltage DC.
The ruggedness and high avalanche capability of 2000V rectifiers are vital for ensuring the converter can withstand voltage spikes and operate reliably for decades in harsh environments.
3.4. Secondary Industrial and Medical Applications
While the EV and renewable energy sectors are key drivers, high-voltage rectifiers play an essential role in many established industrial and medical fields.
3.4.1. Industrial Power Supplies
In heavy industrial equipment for welding, plasma cutting, and electrostatic precipitators (ESPs), rectifiers are used to convert mains AC power into high-voltage DC. This DC power is needed to sustain a powerful electric arc furnace (for example in glass or steel manufacturing) or, in the case of ESPs, to generate a strong electrostatic field for pollution control. In these demanding environments, the ruggedness and long-term reliability of the rectifier are the most critical factors.
3.4.2. Medical Imaging Equipment
Medical systems, notably X-ray generators, use 2000V rectifiers within voltage multiplier circuits. These circuits generate the stable, high-voltage DC power required to function correctly. For these applications, performance consistency and low electrical noise are the driving forces behind the choice of rectifier, with the diode needing to provide a stable output to ensure clear, accurate imaging for diagnostic purposes.
4. WeEn Semiconductors' 2000V Rectifier Solutions
WeEn Semiconductors provides a comprehensive portfolio of high-performance 2000V rectifiers. These are designed to meet the demands of next-generation power systems across the EV, renewable energy, and industrial sectors. These include both advanced silicon and silicon carbide technologies.
WeEn Semiconductors' rectifiers directly improve system-level performance and by focusing on key metrics including low reverse recovery time (trr), low forward voltage (Vf), and excellent thermal resistance (Rth), these components enable designers to achieve higher efficiency, increase power density, and enhance the overall reliability.
4.1. The WND90P20W
The WND90P20W is a robust standard power diode and has been designed for demanding applications like off-board EV chargers and input rectification. It's engineered to handle a high average forward current of 90A and has a high inrush current capability, making it well-suited for systems that experience significant power surges.
4.2. The WND60P20W
The WND60P20W is designed for efficiency and reliability and delivers a 60A average forward current. Key benefits include a low forward voltage drop and minimal leakage current, which help reduce power loss and improve thermal performance in applications like input rectifiers and bypass diodes.
To explore WeEn Semiconductors’full range of 2000V rectifiers, download datasheets, and access detailed application notes, please visit the product page.
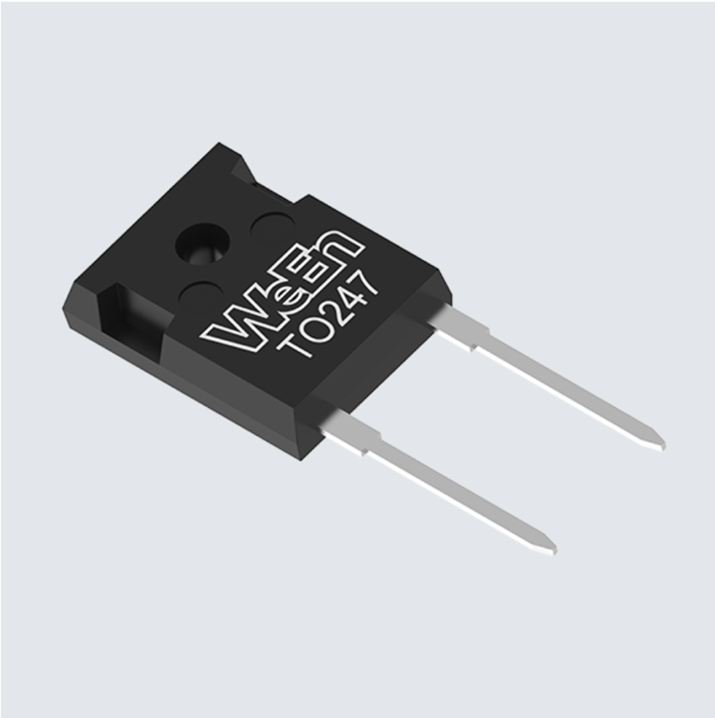

Image: WeEn’s WND90P20W standard rectifier in a TO-247-2L package.
This is designed as a top-level summary of 2000V high-voltage rectifiers. If you would like more detailed information, please see our:
Product pages | Data sheets | Announcements
Keywords: High-voltage rectifier; 2000V rectifier; Standard diode
Latest Articles
-


2025-05-28
WeEn Semiconductors 2025 Selection Guide
Learn more -


2025-05-15
WeEn Semiconductors Releases Super Junction MOSFETs for AI Server and Telecoms Power
Learn more -


2025-05-15
WeEn Semiconductors Unveils 2000V High-Voltage Rectifiers with Improved Efficiency and Enhanced Thermal Performance
Learn more



